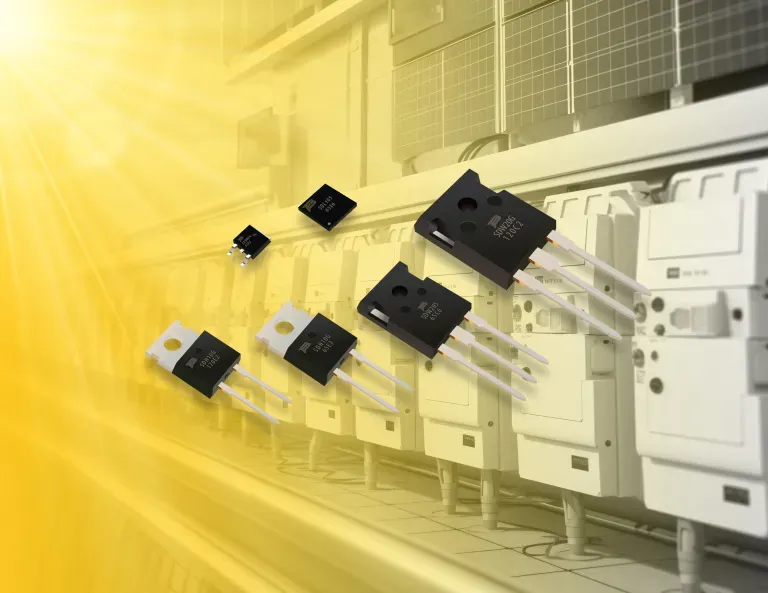
Bourns, Inc. has launched its first 650 V – 1200 V silicon carbide (SiC) Schottky barrier diodes (SBDs), comprised of six models designed to provide excellent current carrying and thermal capabilities and high power density. The BSD series delivers increased performance and reliability for high-frequency applications.
Developed for designs that need higher efficiency and switching performance, the BSD series devices provide high-efficiency power conversion solutions for high-frequency applications that need to reduce their size and lower system cost. Target applications include telecom/server switched-mode power supplies (SMPS), photovoltaic inverters, PC power and motor drives, for reduced thermal resistance and low power loss.
The six new wide-bandgap diodes offer designers a variety of forward voltage, current and package options including TO220-2, TO247-3, TO252 and DFN8×8. They feature low forward voltage (VF) and high thermal conductivity, designed to increase efficiency and lower power dissipation in 650-V and 1200-V solutions.
The series also features no reverse recovery current to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI), enabling these SiC SBDs to significantly lower energy losses, said Bourns. Current ratings range from 6-10 A.
The SiC SBDs are currently available. They are RoHS compliant, halogen free, and lead free. They also feature a flame-retardant epoxy potting compound, meeting the UL 94V-0 standard.