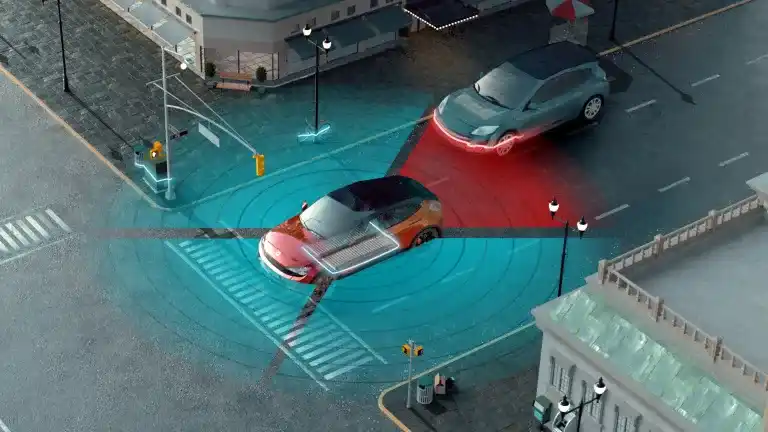
Texas Instruments Inc. (TI) has debuted three new automotive chips at CES 2024 that are designed to improve automotive safety. One of those chips is the AWR2544 77-GHz millimeter-wave (mmWave) radar sensor, claimed as the industry’s first for satellite radar architectures. This satellite radar chip enables higher levels of autonomy by improving sensor fusion and delivering more accurate decision-making in advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS).
Rounding out the product launch are two software-programmable driver chips, the DRV3946-Q1 integrated contactor driver and the DRV3901-Q1 integrated squib driver for pyro fuses, targeting advanced battery management systems (BMS). They offer built-in diagnostics and support functional safety for battery management and powertrain systems. TI is demonstrating the new automotive chips at CES.
The AWR2544 single-chip radar sensor can increase vehicle sensing ranges beyond 200 meters and improve ADAS decision-making. “In satellite architectures, radar sensors output semi-processed data to a central processor for ADAS decision-making using sensor fusion algorithms, taking advantage of the 360-degree sensor coverage to achieve higher levels of vehicle safety,” TI said.
Satellite radar architectures enhance ADAS decision-making by centrally processing radar data from multiple sensors, which improves radar performance, TI said. It also enables radar scalability for ADAS systems with different performance levels and number of sensors around the car.
The AWR2544 automotive satellite radar chip is also the industry’s first with launch-on-package (LOP) technology, which can reduce the size of the sensor by as much as 30% by mounting a 3D waveguide antenna on the opposite side of the printed circuit board, TI said. LOP technology extends sensor ranges beyond 200 meters with a single chip, and in satellite architectures, it enables ADAS systems to make “smarter decisions from farther away.” (Read Are you ready for the emerging automotive radar satellite architecture? for more information.)
The new driver chips support software-defined vehicles by contributing to smarter and more efficient battery management. The two new highly integrated driver chips target requirements for safer and more efficient control of high-voltage disconnect circuits in a BMS or other powertrain system. Both drivers are functional safety-compliant to ISO 26262.
For BMS and other powertrain systems, TI claims the DRV3946-Q1 is the industry’s first fully integrated contactor driver. Key features include a peak-and-hold current controller and low-ohmic power stage that help increase system power efficiency and safety diagnostics to monitor the condition of the contactor. It also supports a range of solenoid types with flexible current control parameters.
The DRV3901-Q1 squib driver delivers an intelligent pyro fuse disconnect system thanks to built-in circuitry that monitors the pyro fuse and provides diagnostic information to the system microcontroller. The pyro fuses reduce design complexity in hybrid and electric vehicle (HEV/EV) BMS systems by replacing discrete circuitry with a single driver. It also improves intelligence and reliability of the disconnect signals by using inputs such as temperature and current signals, TI said. For more information, read How squib and contactor drivers help improve safety and efficiency in HEV/EV battery disconnect systems.
Preproduction quantities of the AWR2544, DRV3901-Q1 and DRV3946-Q1 and evaluation modules (DRV3901-Q1 and DRV3946-Q1) are available for purchase on TI.com.
TI is showcasing its automotive products at CES with demonstrations for ADAS and BMS designs as well as other technologies for applications such as zone architectures, EV charging and energy storage. Visit TI.com/CES for more information.