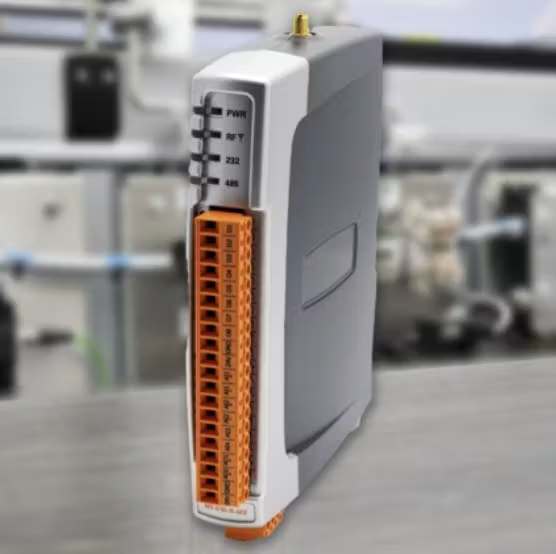
Weidmuller USA has expanded the company’s wireless radio line with the WI-I/O-9-U3 wireless transceiver. This new product combines multi I/O, modem and gateway functionality as well as IoT connectivity. Features include native Ethernet support and comprehensive gateway capabilities for Ethernet and serial protocols, including Modbus TCP/RTU, DNP3 I/O and MQTT + Sparkplug B), and security via AES encryption, advanced IP filtering, multi-level authentication and comprehensive user access and change event logging. The WI-I/O-9-U3 also has long-range communications with 902-928 MHz frequency hopping spread spectrum and up to 1W power, over-the-air diagnostics and configuration, and integrated controls and monitoring with an onboard Logic Engine and an HMI lite dashboard.
HMS Networks launched its Anybus CompactCom B40 Mini, a soldered-on communication interface that complements the Anybus CompactCom 40 series.
The Anybus CompactCom family offers a range of ready-made communication interfaces that can be embedded into any industrial machine or device, enabling connectivity to all major industrial networks. The new Anybus CompactCom B40 Mini adds a soldered-on option to the existing lineup of modules and pluggable bricks.
The Anybus CompactCom B40 Mini includes the following features:
- Compact design: Soldered directly onto the device’s carrier board, it’s 30 percent smaller than the pluggable brick, making it ideal for small devices.
- Efficient manufacturing: Delivered in tape-and-reel and ready for automated production through pick-and-place and Surface-Mount Device (SMD) soldering, it’s designed for high-volume and cost-effective production.
- Versatile network support: Preloaded with PROFINET, Ethernet/IP, POWERLINK, EtherCAT, Modbus TCP, and BACnet Industrial Ethernet networks, or delivered pre-set for a specific network.
These features reportedly enable device manufacturers to simplify product design and production with one design and batch for all protocols.
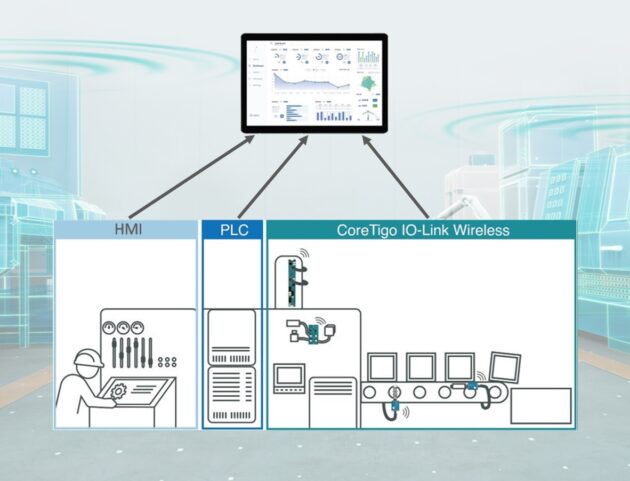
CoreTigo and Raven.ai are collaborating to offer a rapidly deployable solution that enhances production efficiency and operational excellence in manufacturing. The partnership is set to provide manufacturers with fast and easy-to-use tools for improving Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) and optimizing machine performance.
By integrating Raven’s OEE and production tracking software with CoreTigo’s IO-Link Wireless technology, the digital solution reportedly aims to deliver a comprehensive approach to data-driven manufacturing excellence.
CoreTigo’s IO-Link Wireless technology is known for transforming production monitoring and overcoming traditional communication obstacles through the industrial-grade wireless solution. This offers accessibility in challenging and harsh factory environments. CoreTigo is reportedly able to retrofit legacy machines and components with IO-Link Wireless connectivity, without disrupting the production line design or requiring special feedback devices or sensors.
With Raven’s OEE and production tracking software, integrated seamlessly with CoreTigo’s technology, manufacturers gain a complete, contextual overview of production inefficiencies and losses. Raven analyzes data from operators and existing manufacturing systems to identify how people and machines spend their time on the production floor, reportedly accounting for 100 percent of production time.

Industrial facilities require extensive data to optimize revenue and minimize costs, and Moxa has delivered with a new Ethernet switch designed for Network speeds of up to 10 GB.
Moxa has introduced a new lineup of high-bandwidth Ethernet switches specifically tailored for industrial applications. The lineup includes a layer 3 rack mount series designed to deliver speeds of up to 10 GbE, as well as a layer 2 DIN rail mount series offering speeds of up to 2.5 GbE. These switches are designed to cater to the high-speed networking needs of industrial environments.
To enhance production, efficiency, and component quality tracking, industrial facilities require extensive data to optimize revenue and minimize costs. Although numerous high-speed Ethernet switches are available commercially, not all are suitable for the demands of an industrial setting. This is why Moxa has introduced two new families of high-bandwidth industrial switches; The MRX layer 3 rack mount series and the EDS-4000/G4000 series layer 2 DIN rail switches.
The MRX-Q4064 (above) and MRX-G4064 are equipped with 6+2 fans to maintain stable operating temperature ranges. Image used courtesy of Moxa
MRX Series Ethernet Switches
The MRX series of industrial Ethernet switches currently comprises the MRX-Q4064 and the MRX-G4064 and are layer 3 rack-mount devices. These advanced switches are capable of supporting a significant number of field devices with minimal latency and high bandwidth, making them ideal for various industrial environments. They offer flexible port configurations to accommodate diverse industrial setups. Additionally, both switches are designed to regulate temperature with 8 fan modules and feature a dual power supply for effective power management and seamless, uninterrupted operations and bridge IT and OT networks.
Each MRX features a modular design and is well-suited for large industrial networks. Both the MRX-Q4064 and MRX-G4064 can accommodate up to 64 ports.
Data in the 21st Century is required faster and in higher volume than ever before. Image used courtesy of Adobe Stock
The MRX-Q4064
(16) 10GbE built-in
(48) 2.5GbE ports supported through modules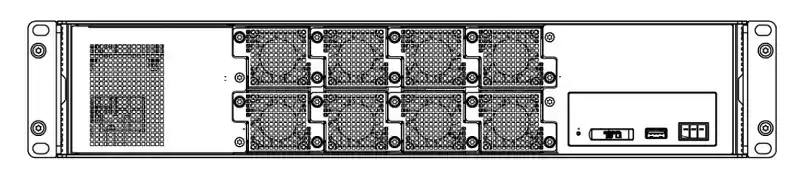
Dimensional drawing of rack mount options for the MRX series of Ethernet switches. Image used courtesy of Moxa
The MRX-G4604
(8) 10GbE ports built-in
(56) 2.5GbE ports support through modules
The MRX device is equipped with a command line interface (CLI) for streamlined management, an out-of-band management (OOBM) port for secure remote access, and port mirroring for efficient monitoring and security management.
The EDS-4000/G4000 Series
This comprehensive portfolio of layer 2 DIN-rail Ethernet switches comprises 68 different models and has uplink options of up to 2.5GbE. These layer 2 switches are designed to build a secure and reliable industrial network with the MRX-G4064 and MRX-Q4064 series switches. All EDS-4000/G4000 series switches are compliant with the IEC 62443-4-2 industrial cybersecurity standard to block any malicious activity with DHCP snooping features.
The EDS-4008 has a compact and modular design that allows easy adaptation to suit the customer's needs. Image used courtesy of Moxa
The EDS-4000/G4000 series of switches offers a wide range of advanced features designed to elevate your networking capabilities.
Familiarity with Moxa’s technology affirms that the EDS switch is equipped to support Turbo Ring, Turbo Chain, and MRP technologies, thereby ensuring network redundancy. Moreover, these devices are designed to be compatible with PROFINET, Ethernet/IP, and Modbus TCP communication protocols, enabling them to be customized to align with the specific requirements of individual systems.
Pepperl+Fuchs has launched the Smart-Ex 03, a rugged smartphone designed for hazardous areas. Approved for Zone 1/21 and Div. 1, it operates on Android 13 and supports 5G, Wi-Fi 6, and eSIM technologies, ensuring global connectivity for communication and collaboration. It features up to 128 GB internal memory. Equipped with a Qualcomm QCM6490 processor, the Smart-Ex 03 facilitates various applications including digital workflows, asset management and augmented reality. The device features an advanced camera tailored for industrial needs and offers desktop mode for direct connectivity to monitors and peripherals. Security features include a fingerprint sensor and continuous device monitoring.

The new product reduces antenna height by 50% compared to competitive offerings.
In space-constrained applications like global navigation satellite systems (GNSS), designers often face a tradeoff between antenna height and performance. To solve this issue, Taoglas recently announced a new antenna solution, the HP5354.A, that leverages a unique “patch-in-a-patch” architecture to reduce antenna height and weight.
A Patch Antenna for Positioning and Tracking
Taoglas describes the HP5354.A as a low-profile, multi-band GNSS L1/L5 patch antenna designed specifically for modern positioning and tracking applications.
This multi-band antenna (datasheet linked) supports a range of frequencies:
- GPS: L1 at 1,575.42 MHz and L5 at 1,176.45 MHz
- GLONASS: G1 at 1,602 MHz
- Galileo: E1 at 1,575.24 MHz and E5a at 1,176.45 MHz
- BeiDou: B1 at 1,575.42 MHz and B2a at 1,176.45 MHz
The HP5354.A achieves an efficiency of 52.6% at GPS L1 and 51.7% at Galileo E1. The antenna offers an axial ratio of 1.79 dB, translating to high signal clarity and strength. The average gain of the antenna is -2.79 dB at GPS L1, with a peak gain of 2.61 dBi.

HP5354.A radiation pattern at 1,575 MHz. Image used courtesy of Taoglas
Measuring at a compact 35 mm x 35 mm x 4 mm, the product incorporates a ceramic patch within a patch design, a technique that enhances signal reception and gain across multiple GNSS bands. It also features a dual-feed solder mount configuration that supports right-hand circular polarization (RHCP) for reliable GNSS applications. The antenna employs two orthogonal feeds for the L1 band and a separate feed for the L5 band, combined using a hybrid coupler (HC125A) for high axial ratio and gain.
This antenna's design includes a recommended 70 mm x 70 mm ground plane to achieve peak performance. Taoglas also offers the TFM.100B front-end module, which incorporates a SAW/LNA/SAW/LNA topology to mitigate out-of-band interference and maintain a low-noise figure.
Taoglas' Patch-in-a-Patch Architecture
A patch antenna is a type of microstrip antenna that includes a conductive patch of metal (such as copper or gold) placed on a dielectric substrate with a ground plane on the opposite side. The antenna itself is normally flat and mounted on a substrate, while the conductive patch acts as the radiating element and is usually rectangular or circular—although other shapes can be used to achieve specific performance characteristics.
Patch antennas operate based on the principles of resonant cavities. When an RF signal is fed into the patch, it generates an electromagnetic field between the patch and the ground plane. This field resonates, producing a standing wave pattern. The edges of the patch radiate this energy into free space, creating the antenna's radiation pattern. The radiation is typically broadside, meaning it is perpendicular to the plane of the patch, providing a directional beam for many applications such as satellite communications, GPS, and WLAN.

The architecture of a basic patch antenna. Image used courtesy of Science Direct (Rouphael)
Patch antennas are valued for their simplicity, low profile, ease of fabrication, and integration into printed circuit boards (PCBs). They are lightweight and can be manufactured in large quantities at low cost. Additionally, patch antennas can be designed to operate at multiple frequencies or support dual polarization, enhancing their versatility in different applications.
Taoglas' "patch-in-a-patch" is an advanced architecture built to improve the performance of standard patch antennas. In this design, a smaller patch is embedded within a larger patch, enhancing bandwidth and multi-frequency operation without significantly increasing the antenna's overall size. The inner patch resonates at higher frequencies, while the outer patch covers lower frequencies. This dual-layer structure can provide better impedance matching and gain, making it suitable for applications requiring wideband or multi-band performance.
Saving Space Without Sacrificing Performance
As technology advances, the demand for compact, high-performance components in space-constrained environments continues to grow. The Taoglas HP5354.A "patch-in-a-patch" antenna features an innovative antenna design that Taoglas hopes can address the challenge of reducing size while maintaining exceptional performance.

STMicroelectronics designed its embedded SIM (eSIM) to comply with new GSMA eSIM protocols for IoT deployments.
STMicroelectronics has released the ST4SIM-300, which, according to the company, is the first embedded SIM (eSIM) device that complies with the new GSMA eSIM IoT Technical Specification (SGP.32).
Building upon prior eSIM standards, the new IoT protocols within the SGP.32 specification allow system operators to remotely program device subscriber identities over the air (OTA) to ensure device connectivity across global networks.
ST designed the ST4SIM-300 for small IoT devices like asset trackers, utility meters, and portable healthcare devices. In addition to its interoperability across global 4G and 5G networks, the new eSIM is also well suited for lower data rate applications that use narrow-band IoT (NB-IoT) or other bandwidth-constrained networks.
The new eSIM and associated IoT protocols are designed to simplify a system operator’s management of a fleet of connected devices. It is a plug-and-play solution that even smaller integrators can implement.
The First eSIM for SGP.32
The ST4SIM-300M (datasheet linked) is fully compliant for remote SIM provisioning per GSMA eSIM IoT standards. This means it is compatible with 2G, 3G, 4G (LTE), CDMA, NB-IoT, and CAT–M networks. For OTA updates, the small, 8-pin chip communicates with the device modem via an ISO/IEC 7816 protocol (I/O, RST, CLK) to relay the new subscriber ID to the eSIM. For WLCSP package options, ST offers an embedded secure element (eSE) for secure storage and cryptographic services. In addition to PCB mountable DFN and WLCSP packages, the ST4SIM-300M eSIM is also available in traditional SIM card plugin configurations.
The IoT-compliant ST4SIM-300 enables the remote swapping of devices from one cellular network operator to another without the need to physically access them.

Updating the ST4SIM-300 eSIM profile
To do this, the device fleet manager requests profiles from the new mobile network operator (MNO). The MNO delivers the new profiles to its subscription manager data preparation plus (SM-DP+). The IoT device operator then sends a “Download” command to the eSIM IoT remote manager (eIM) that allows the device to download the new profiles from the MNO’s SM-DP+ server to the IoT profile assistant (IPA). The new subscriber ID is then relayed to the ST4SIM-300 via the device modem.

Overview of the eSIM architecture.
The GSMA IoT protocols govern all interactions between the IoT device manager and the MNOs, enabling seamless coordination among network participants, including device managers and network operators.
What Is an Embedded Subscriber Identity Module (SIM)?
For cellular networks, a subscriber identity module (SIM) card is a small removable card that gives a device (traditionally a phone) a unique numerical identifier within the network. An embedded SIM (eSIM) is a small integrated circuit embedded into a phone, meter, or other IoT device during the manufacturing process that serves the same purpose as the traditional SIM card.

The evolution of SIM and eSIM
Some of the benefits of an eSIM are lighter, more compact devices. eSIMs are also more reliable in remote and potentially harsh industrial environments.
eSIM IoT Standards (SGP.32)
In 2013, the Global System for Mobile Communications (GSMA) established remote eSIM provisioning standards for automotive OEMs and machine-to-machine (M2M) service providers. In 2016, the M2M standard was followed by standards for consumer smartphones. In July 2023, the GSMA released the eSIM IoT Technical Specification (SGP.32) to ease the adoption of remote SIM provisioning for connected device system integrators.
The recent IoT standard introduces powerful configuration capabilities that allow device OEMs to manage their own device subscriber identities rather than the telecom operator. With eSIM IoT protocols, a device can be easily OTA configured for operation in any cellular network worldwide.
For example, asset trackers monitoring global shipments can pass from one cellular network to the next without physical access to the device, ensuring continuous connectivity as a shipment transits the globe.
ST believes its eSIM can help secure asset tracking and data handling from billions of devices in cities, smart homes, and industrial applications.
All images used courtesy of STMicroelectronics.

The new microcontroller adds robust wireless connectivity and offloading to bolster the host processor.
Last week, Infineon added to a new family of connected microcontrollers (MCU) to its AIROC family for IoT applications. The ultra-low-power CYW55913 MCUs integrate support for Wi-Fi 6/6E, BLE 5.4, and Matter into one device, making it useful for smart homes, industrial IoT, and portable devices.
The new family includes this wireless connectivity to overcome the modern challenges of device density, interference, and power consumption.
A Wireless MCU for Modern IoT Standards
At its core, the CYW55913 family features a 192-MHz Arm Cortex-M33 processor with TrustZone security. This compute is complemented by 2 MB of ROM and 768 KB of SRAM. The device offers peripherals including a 12-bit, seven-channel analog-to-digital converter (ADC), a rich set of interfaces (SDIO, SPI, UART, I2C, I2S, PDM, and GPIOs), and Quad-SPI (QSPI) Flash/PSRAM with execute-in-place (XIP) and on-the-fly (OTF) features.

Block diagram of the CYW55913. Image used courtesy of Infineon
The CYW55913 supports tri-band Wi-Fi 6E across 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz bands, with a 20-MHz channel bandwidth and Wi-Fi PHY data rates up to 143 Mbps. Integrated power amplifiers deliver up to +24 dBm Tx power. Its Bluetooth Low Energy 5.4 extends features like LE Long Range, LE 2 Mbps, and extended advertising. Bluetooth LE transmission power options range from +4 dBm to +19 dBm, with a sensitive -111.5 dBm Rx for Long Range mode.
The MCU operates between 3.0 V to 3.6 V and across a temperature range from -40°C to 85°C. It comes in a compact WLBGA form factor measuring just 3.57 mm x 5.32 mm with a 0.35 mm pitch.
The Technology Behind Wi-Fi 6E
Wi-Fi 6E can be thought of as an extension of the Wi-Fi 6 standard, improved to provide additional spectrum, more channels, less interference, and higher performance.
Wi-Fi 6E's primary distinction lies in its operation within the 6-GHz band, which is less crowded than the traditional 2.4-GHz and 5-GHz bands. Operating in the 6-GHz band, Wi-Fi6E adds 1,200 MHz of spectrum to the existing 2.4-GHz and 5-GHz bands, resulting in up to seven additional 160-MHz channels.
The technology uses Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) and Multi-User Multiple Input Multiple Output (MU-MIMO) to increase efficiency and capacity. OFDMA divides the spectrum into smaller channels, allowing multiple devices to communicate simultaneously without waiting for their turn. Meanwhile, MU-MIMO allows the router to communicate simultaneously with multiple devices, thereby improving overall network throughput and reducing latency.

Wi-Fi 6E introduces the 6-GHz band for the first time. Image used courtesy of Aruba Networking
Wi-Fi 6E may have a notable impact on the IoT. First, the expanded spectrum and additional channels reduce the interference and congestion of a growing number of IoT devices to enable more reliable and higher-speed connections. Additionally, Wi-Fi 6E includes advanced features like Target Wake Time (TWT), which schedules device check-ins to reduce power consumption. Such features are designed with battery-powered IoT devices in mind and are extremely useful for extending device operational life and reducing maintenance.
Infineon hopes that its CYW55913 MCU, which supports Wi-Fi6E, can be a powerful new tool for design engineers, allowing for multi-protocol support in one compact, power-efficient solution.
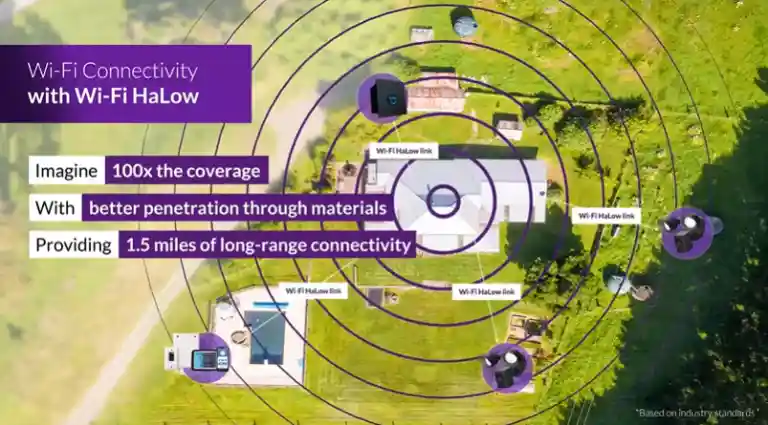
Startup Morse Micro, a fabless Wi-Fi HaLow silicon vendor, along with its partners, showcased several new Wi-Fi HaLow-enabled devices at CES 2024. These include a wireless home security camera with AI, edge AI security cameras, routers for long-range IoT and remote-area connectivity solutions. Morse Micro is an EE Times Silicon 100 startup to watch.
Wi-Fi HaLow technology is the first Wi-Fi standard that is specifically tailored for IoT applications. The Wi-Fi HaLow 802.11ah standard, operating in the sub-GHz frequency band, delivers a combination of benefits, including lower power consumption, high data rate, extended range, higher throughput and advanced security. It also offers lower deployment costs and interoperability.
Morse Micro, in collaboration with its partners, will demonstrate Wi-Fi HaLow technology breakthroughs across a range of IoT applications at CES. Here are few of the latest new products adopting Wi-Fi Halow.
AI-enabled smart home security camera
NXP Semiconductors N.V. has expanded its automotive radar one-chip family, introduced this time last year, with the launch of the new SAF86xx. The device monolithically integrates a high-performance radar transceiver, a multi-core radar processor and a MACsec hardware engine for secure data communication over automotive Ethernet.
The radar one-chip, together with NXP’s S32 high-performance processors, vehicle network connectivity and power management, delivers a full system solution that readies the path for software-defined radar, from smart sensors to future streaming sensors, NXP said. This includes 360-degree sensor fusion, better sensor resolution and AI-based object classification.
The highly integrated 76 to 81 GHz radar SoC is used for streaming low-level radar sensor data at up to 1 Gbit/s. NXP said it will help carmakers optimize next-generation ADAS partitioning for software-defined vehicles and provide a smooth transition to new architectures. It also will allow OEMs to introduce new software-defined radar features during the lifetime of the vehicle with over-the-air (OTA) updates.
“Using our new SAF86xx radar one-chip family, OEMs can quickly and easily migrate their current radar platforms to new software-defined vehicle architectures,” said Steffen Spannagel, SVP and GM, ADAS, NXP Semiconductors, in a statement. “A network of connected radar sensors with software-defined functions on a dedicated S32R radar processor in a distributed architecture can enhance radar-based perception to support advancements in autonomous driving. That includes 360-degree sensing, more powerful AI-based algorithms and secure OTA software updates.”
The SAF86xx shares a common architecture with the SAF85xx introduced last year and also leverages 28-nm RFCMOS performance for improved radar sensor capabilities, compared to prior-generation 40-nm or 45-nm products. Other features include an extended detection range beyond 300 meters and more reliable detection of small objects like curb stones as well as vulnerable road users including cyclists and pedestrians.
The SAF86xx supports NCAP safety functions and advanced ADAS and autonomous driving applications, including advanced comfort features for SAE levels 2+ and 3. It is developed in accordance to ISO 26262 Safety Element out of Context (SEooC) methodology supporting ASIL Level B, in accordance to ISO/SAE 21434 (as a component-out-of-context) and meets the latest security requirements through its HSE security engine
The SAF8xxx family, featuring the SAF86xx and SAF85xx, can be tailored for OEM applications. It supports a range of sensor outputs, including object, point cloud-, or range-FFT-level data for smart sensors in today’s architectures and streaming sensors in future distributed architectures, NXP said. It is sampling now for alpha customers.
NXP also announced that automotive electronics supplier HELLA will use NXP’s SoC family for its 7th generation radar portfolio, including front, rear, corner and side radar. NXP’s radar portfolio is on display at CES 2024, LVCC, booth CP-18.